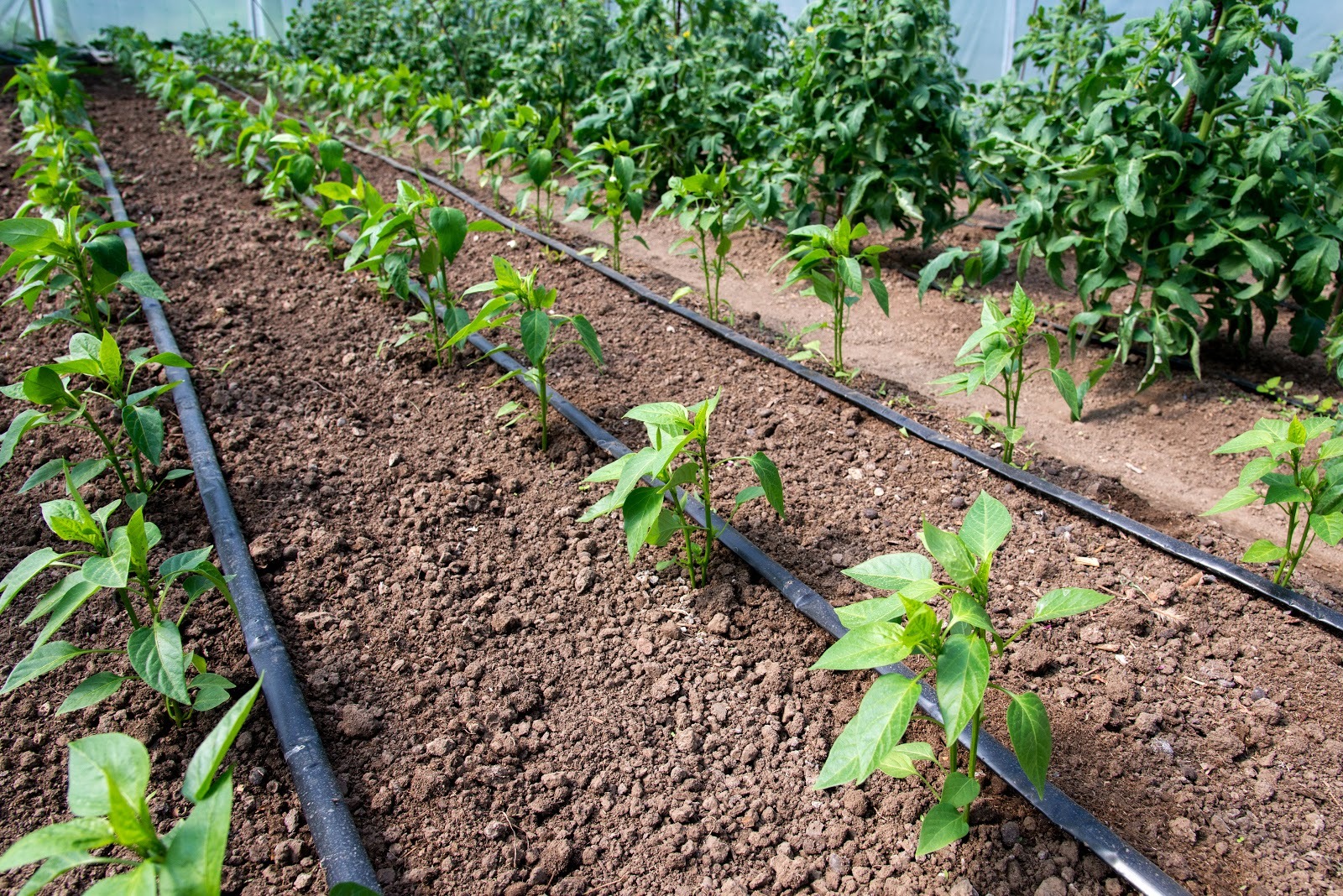
What Is Drip Irrigation?
Drip irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation, involves applying water directly to the soil near the plant root zone through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters. This ensures uniform distribution of water with minimal waste.

Key Components of a Drip Irrigation System
A drip irrigation system is relatively simple but requires correct setup and maintenance to operate effectively. The main components include:
How Drip Irrigation Works in the Field
The process is straightforward but highly effective:
Water Delivery
Water is pumped from the source into the mainline.
Filtration
Filters remove sediment, algae, or other particles that could clog emitters.
Pressure Regulation
The system stabilizes water flow so that each plant receives a consistent amount.
Distribution
Drip tape or tubing delivers water drop by drop directly to the soil near plant roots.
Absorption
Water infiltrates slowly, ensuring that roots absorb moisture efficiently without waterlogging.
For crops like vegetables, fruits, vineyards, and orchards, this system ensures healthy root development and uniform plant growth.
Benefits for Farmers
Farmers worldwide adopt drip irrigation because it addresses common agricultural challenges:
Water Efficiency
Saves 30–50% water compared to sprinkler or flood systems.
Improved Yields
Consistent water availability leads to healthier crops and higher productivity.
Reduced Weed Growth
Since water is applied only to plant rows, weeds receive less moisture.
Labor Savings
Automated drip systems reduce the need for manual watering.
Soil Health
Prevents erosion and nutrient leaching caused by excessive surface irrigation.
Common Problems and Solutions
Even the best drip systems face operational challenges. Here are the most frequent issues and how to fix them:
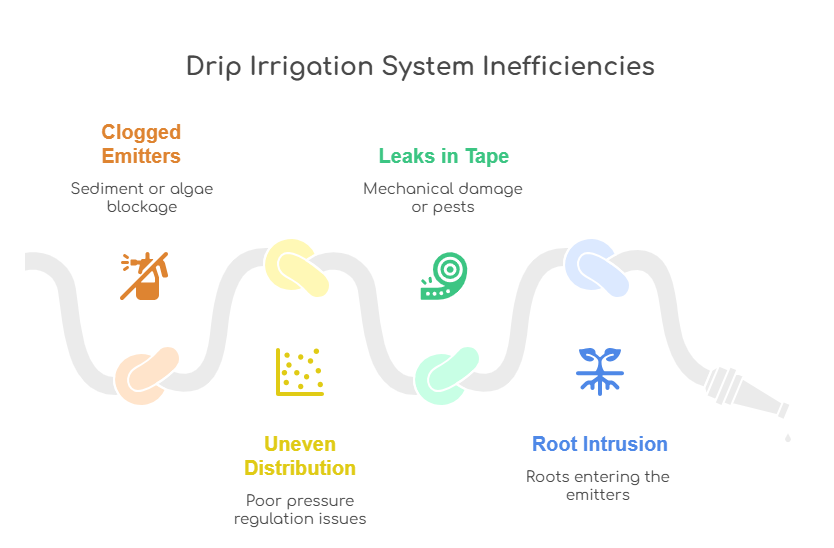
By anticipating these issues, farmers can keep their irrigation systems running efficiently throughout the growing season.
Practical Tips for Farmers
- Test water quality before installation to ensure proper filtration.
- Plan the field layout carefully to minimize water pressure drops.
- Use seasonal maintenance: flush lines, replace worn-out drip tape, and check seals.
- Combine with fertigation (nutrient delivery through irrigation water) for maximum efficiency.
Pandora's Role in Supporting Farmers
At Pandora, we specialize in manufacturing reliable drip irrigation tape and accessories designed for both garden and farm-scale use. With customizable solutions for wholesalers, distributors, and farm operators, our systems are engineered for durability, easy installation, and compatibility with diverse crop needs.

👉 Contact us for more farming and irrigation solutions







